Information on this site shall be considered as holistic, alternative and spiritual advice only. For medical advice and treatment a GP, medical professional and/or Certified Hijama Therapist should be consulted. In all circumstances where lifestyle changes, supplements, or other foods are suggested your GP should be consulted. Client Safety is the number one priority.
Cupping Points Treatment Plan for Liver and Gall Bladder Disease
Allow 2-4 weeks between sessions – longer if required. Hijama Points shown for each session should ONLY be used to guide the therapist. Body size, cup size, and any other conditions need to considered and appropriate care and attention taken. The number of sessions shown can be increased or reduced depending on the condition of the client.
Complete Treatment Plan
Click here for Session 1Click here for Session 2
Click here for Session 3
Click here for Session 4
Click here for Session 5
Use the standard hijama points as an addition or as separate standalone sessions.
Standard Wet Points – 1,55,6,48,41,42,46,51,122,123,124
Click here for Hijama Points on the front of the bodyClick here for Hijama Points on the back of the body
If the client has a complicated history and numerous concerns then it is a good idea to use our online consultation service – click here.
Which body part or function is involved in Liver and Gall Bladder Disease?
The liver and gallbladder are the two accessory organs of the digestive tract, which carry out a multifunctional role that supports digestion and maintains body chemical balance. The liver is essentially the largest gland. It’s located under the diaphragm and found mostly in the upper right side of your abdominal cavity. It’s a big organ with various vital functions, it should not be offended that the liver also regulates many metabolic and regulatory functions for your body. By it, we see that the liver is an important organ of GIT because it produces bile. The liver consists of two lobes and receives its blood supply mainly from the hepatic portal vein. This organ also regulates the function of detoxification of the body.

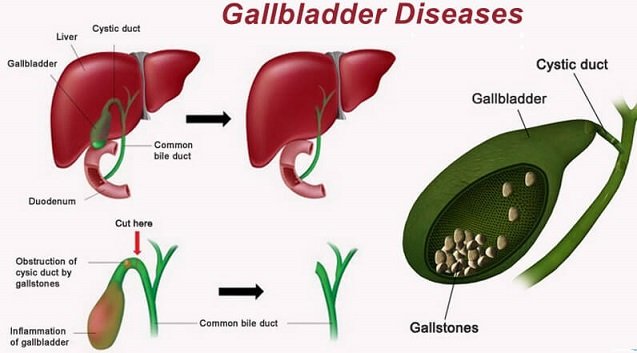
Gallbladder
Found inferiorly to the liver, being about the storage and release of bile into the duodenum. This bit organ carries out the metabolic, exocrine, and endocrine roles. The process of breakdown of protein is taking place in it, which maintains osmotic pressure, transports micronutrients, and acts in blood clotting. Many important metabolic nutrients are stored in the liver like Vitamins A, D, and K, iron, and glycogen. They are released into the bloodstream when needed.
Liver
Also improves the action of various endocrine hormones and synthesizes bile, which is stored in the gallbladder. The main gallbladder function is to preserve and acidify bile. While eating a meal, the presence of fats and proteins in the intestines stimulates the release of hormones causes simultaneous contraction of the body and relaxation of the neck of the gallbladder.
What are the symptoms and effects of Liver and Gall Bladder Disease on the body?
The abnormal functioning of the liver is characterized by the term ‘Cirrhosis’ that means permanent scarring of the liver. In this condition, the healthy liver cells are displaced by scar tissue that cannot fulfill any liver function.
Major symptoms of liver disease include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Right upper quadrant abdominal pain
- Jaundice
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Weight loss
Damage
Though, since there are numerous liver diseases, the symptoms tend to be specific for that illness until late-stage liver disease and liver failure occurs. The liver can be damaged in many ways. The hepatic Cells can become inflamed, for example, hepatitis. Bile flow can be restrained, for example, cholestasis. The accumulation of Cholesterol or triglycerides can cause major liver damage, for example, steatosis. Blood flow to the liver may be endangered. Liver tissue can be damaged by certain chemicals and minerals, or penetrated by abnormal cells, like cancer cells. Alcohol abuse and liver disease The most common cause of liver disease is an uncontrolled intake of alcohol. Alcohol is directly lethal to liver cells and can cause liver inflammation, commonly called alcoholic hepatitis. In chronic alcohol abuse, fat deposition occurs in liver cells affecting their functions.
Gallbladder disease
The most common disease associated with the gallbladder is gallstones. Gallstones develop when chemicals in the bile (such as cholesterol, bile salts, and calcium) or components from the blood (like bilirubin) form hard matter that blocks the passages to the gallbladder and bile ducts. Gallstones also tend to form when the gallbladder doesn’t clear entirely or often enough. They can be small or large depends on the severity of the condition. It may show no signs or symptoms. If a gallstone occupies in a duct and causes a blockage, the arising signs and symptoms may include:
- Sudden and fast increasing pain in the upper right part of your abdomen
- Sudden and fast intensifying pain in the center of your abdomen.
- Back pain between your shoulder blades Pain in the right shoulder
- Nausea and vomiting.
What changes in diet can help improve symptoms of Liver and Gall Bladder Disease?
Liver Disease: There are two most common types of fatty liver disease 1) alcohol-induced and 2) nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. The most beneficial and easiest way to treat fatty liver disease, regardless of type, is with diet. Generally, the diet for fatty liver disease should include:
- fruits and green vegetables
- high-fiber plants and whole grains
- Low level of sugar, salt, trans fat, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fat
- nalcohol
- Oatmeal
- Walnuts
- Fish
- Sunflower seeds Milk and low-fat dairy Olive oil Garlic help reduce body fat
Gallstones: Increase intake of high fiber foods, green vegetables, peas, grains, fish. These are the food that can help to lower the risks and complications of gallstones
Changes in lifestyle which can help Liver and Gall Bladder Disease
1. Liver Disease:
Although, Lifestyle changes cannot treat any liver disease. But they can improve the symptoms and help in avoiding further damage. General lifestyle changes that can support the life of your liver are mentioned:
- Avoid alcohol.
- Balanced diet.
- Avoid raw seafood
- Take the right amount of protein.
- Take vitamin or mineral supplements if the doctor recommends.
- A low-salt diet
- Raise the Legs to ease Any Swelling
2. Gallstones:
- Active lifestyle
- Herbs and supplements
- Maintain healthy weight
- Take anti-inflammatory diet
- Eat bitter vegetables
Possible alternative remedies for Liver and Gall Bladder Disease
Some of the remedies that can help boost up your liver functions:
- Garlic and Onions: Contain compound that helps prevent fat deposition in the liver.
- High-Fiber Diet: Food high in fiber supports the liver function properly, also helps to excrete fatty toxins out of the body.
- Pomegranate Tea: Pomegranate is a super detox food that the liver, a strong antioxidant, high in Vitamin C, calcium, and potassium.
- Dry Massage: Stimulate liver function with a dry massage of the foot soles with a brush. Do this around 40-50 times. this is an impressive method to stimulate lymphatic. Gallbladder: Olive oil and sunflower: Olive oil and sunflower: one study looked at e role of olive oil and sunflower oil on gallstones. The experimenters found that while olive oil had an impact on bile consumption did not affect the gallstones.