Information on this site shall be considered as holistic, alternative and spiritual advice only. For medical advice and treatment a GP, medical professional and/or Certified Hijama Therapist should be consulted. In all circumstances where lifestyle changes, supplements, or other foods are suggested your GP should be consulted. Client Safety is the number one priority.
Hijama / Cupping Points Treatment Plan for Convulsions or Fits
Allow 2-4 weeks between sessions – longer if required. Hijama Points shown for each session should ONLY be used to guide the therapist. Body size, cup size, and any other conditions need to considered and appropriate care and attention taken. The number of sessions shown can be increased or reduced depending on the condition of the client.
Complete Treatment Plan
Click here for Session 1Click here for Session 2
Click here for Session 3
Click here for Session 4
Click here for Session 5
Click here for Session 6
Click here for Session 7
Use the standard hijama points as an additional or as separate standalone sessions.
Standard Wet Points – 1,55,101,36,32,107,114,11,12,13
Click here for Hijama Points on the back of the bodyIf the client has a complicated history and numerous concerns then it is a good idea to use our online consultation service – click here.
Which body part or function is involved in Convulsions or Fits?
Neurons of the CNS convey messages via rapid electrical impulses that let the brain to correspond behavior, sensation, thoughts, and emotion. Muscles act when bran commands it to. Motor neurons, which are single nerve cells of the spinal cord, are the only way the brain communicates to muscles. When a motor neuron of the spinal cord fires, an impulse runs out from it to the neuron’s muscles. When the impulse travels down the axon to the muscle, a chemical is ejected at its ending. Muscles consists of long fibers attached longways by a ratchet mechanism, the kind of mechanism that enables the two parts of an extension ladder to glid past each other and then lock in a particular position. When the chemical impulse from the motor neuron strikes the muscle, it causes muscle fibers to rachet past each other, extending over each other more so that the muscle gets shorter and thicken. When the impulses from the nerves stop, the muscle fibers relax back to their actual positions.
Each motor neuron communicates to just one muscle, say the bicep on the front of your upper arm that raises your forearm, or to the triceps, the one on the back that causes extension in your forearm. In the cerebral cortex, the orders in the neurons there characterize coordinated movements, like holding up the cup of tea, hit the football, salute. The cortex then relates to a kind of console in the spinal cord that overlaps the motor neurons. This console expands arm posture in space, up-down, left-right. Each needed arm position then is taken as a compilation of certain commands to each motor neuron and muscle. Any disturbance in the electric activity of the brain due to any disease or ailment can result in convulsions and fit also known as seizures. Seizures are more common than anyone might think. Seizures can occur after a stroke, a severe head injury.
What are the symptoms and effects of Convulsions or Fits on the body?
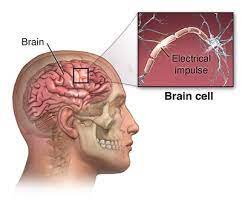
In medical terminology convulsions or fits are called seizures, which happens when there is an abrupt burst of electrical activity in the brain temporarily hindering the normal communicating processes.
The brain affects the whole of the body and so where the convulsions arise in the brain, will involve different areas of the body. There are several types of seizures and a lot of different causes. Any head trauma or tension to the brain can cause seizures, as can brain tumors, malignancy, malaria, eclampsia in pregnancy, etc. It is very common for babies and young children to undergo febrile convulsions. These are convulsions caused by an increased temperature when they are sick. Seizures are very horrible, yet these are hardly life-threatening. Observing the patient’s behavior during convulsions can be useful to neurologists. A sign of epilepsy is made when someone has had at least one light seizure that cannot be associated with any other cause. Fits, seizures, or convulsions can result in harsh out-of-control movements. The causality may undergo absence seizures, where they become strict and unresponsive, full smashing around tonic / clonic fits or anything in between.
Symptoms associated with seizures:
There are several types of seizures, which vary in symptoms and severity. Seizure types depend on where in the brain they started and how far they dissipate. Most seizures stay from 30 seconds to two minutes. A seizure that prolongs a stay than five minutes is a severe emergency. With a seizure, signs and symptoms can vary from mild to severe and change depending on the type of seizure. Seizure signs and symptoms may include:
- Momentary confusion
- A gawking spell
- Unmanageable jerking movements of the arms and legs
- Loss of consciousness or awareness
- Cognitive or emotional symptoms, such as fear, terror, anxiety, or déjà vu.
What changes in diet can help improve symptoms of Convulsions or Fits?
The commonly recommended diet for people with seizures and epilepsy is specified with the name “classic” ketogenic diet. It is a special high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that controls seizures in some people suffering from epilepsy. It is prescribed by a physician and carefully monitored by a dietitian. It is usually utilized in children with seizures that do not improve by medications.
Changes in lifestyle which can help Convulsions or Fits
Lifestyle modifications can include:
- Enough sleep – Fatigue is one of the most often seizure triggers, and lack of sleep can make the brain weaker to misfiring.
- Avoiding drugs and alcohol – These can be stimulated seizures in patients with epilepsy. Even one or two small intakes can induce seizures.
- Minimizing emotional stress – Although there is no decisive evidence that stress causes seizures, those who maintain healthy stress levels have noted that they believe it decreases their risk.
Possible alternative remedies for Convulsions or Fits
Till now, there’s not much scientific proof that herbal remedies can successfully treat convulsions and fits. Most suggestions are anecdotal, but maybe worth trying with your GPs permission. Some of the herbs that are used most often for convulsions are:
- Burning bush
- Groundsel
- Hydrocotyle
- Lily of the valley
- Mistletoe
- Mugwort
- Peony
- Skullcap
- Tree of heaven
- Valerian