Information on this site shall be considered as holistic, alternative and spiritual advice only. For medical advice and treatment a GP, medical professional and/or Certified Hijama Therapist should be consulted. In all circumstances where lifestyle changes, supplements, or other foods are suggested your GP should be consulted. Client Safety is the number one priority.
Cuppinng / Hijama Points Treatment Plan for Varicose Veins
Allow 2-4 weeks between sessions – longer if required. Hijama Points shown for each session should ONLY be used to guide the therapist. Body size, cup size, and any other conditions need to considered and appropriate care and attention taken. The number of sessions shown can be increased or reduced depending on the condition of the client.
Complete Treatment Plan
Click here for Session 1Click here for Session 2
Click here for Session 3
Standard Wet Points – 1,55,28,29,30,31,132
Click here for Hijama Points on the back of the bodyClick here for Hijama Points on the lower limbs of the body
If the client has a complicated history and numerous concerns then it is a good idea to use our online consultation service – click here.
Which body part or function is involved in Varicose Veins?
Veins are a type of blood vessel that brings deoxygenated blood from different organs of your back to your heart. These are much more distinctive from your arteries, which carry oxygenated blood from your heart to the rest of your body. Deoxygenated blood that runs through your veins is collected within small blood vessels called capillaries. Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in the human body. Oxygen diffuses through the lining of your capillaries to your tissues. Carbon dioxide can also enter your capillaries from the tissue before reaching your veins.
The walls of your veins are composed up of three different layers:
- Tunica external. This is the external layer of the vein wall, and it’s also the thickest layer. It’s largely made up of connective tissue. The tunica externa also encloses tiny blood vessels called vasa vasorum that supply blood to the lining of your veins.
- Tunica media. The tunica media is the middle layer. It’s fragile and comprises a huge amount of collagen.
- Tunica intima. This is the internal layer. It’s a thin and single layer of endothelium cells and some connective tissue. This layer sometimes contains one-way valves. These valves prohibit blood from flowing backward.
Veins are often classified based on their region and any distinctive features or functions. Pulmonary and systemic veins – Your body distributes blood on two distinct tracks called the systemic circuit and the pulmonary circuit. Veins are based on the circuit they originate in:
- Pulmonary veins. The pulmonary circuit delivers deoxygenated blood from your heart to your lungs. They’re different because they take oxygenated blood.
- Systemic veins. The systemic circuit delivers deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body back to your heart, where it then joins the pulmonary circuit for oxygen. Most veins belong to systemic veins.
What are the symptoms and effects of Varicose Veins on the body?

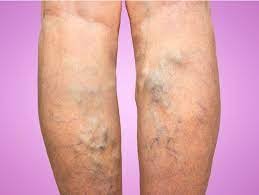
The varicose vein is a condition in which veins become twisted, enlarged, and show dark discoloration over the skin. Any small vein may become varicose, but the most commonly affected veins are those in your legs. The general reason is, standing and walking continuously increases the pressure in the veins of your lower body. The condition is very common, particularly in women. Around 25 percent of the adult population has varicose veins.
Varicose veins usually do not cause us any pain. But In severe cases, it causes symptoms like:
- Veins that are dark purple or blue discoloration.
- Veins appear twisted and swelling; they are often like wires on your legs.
- Cause achy or heavy feeling in your legs
- Inflammation, pulsation, muscle cramping, and swelling in your lower legs
- Intense pain after standing or walking for a long time
- Itching around veins
- Skin scar around a varicose vein
Cause: vein complications that involve smaller blood vessels are telangiectasia and spider veins. According to the structure of the vein, it has one-way valves inside that open and close to keep blood flowing toward the heart. Though, weakened or injured valves or walls in the veins can cause blood to pool and cause thrombosis and even reverse its flow. This is called reflux. The veins may grow bigger and become irregular, resulting in varicose veins. In serious cases, a varicose vein may rupture, or forms varicose ulcers on the skin. These will require urgent treatment. If the patient has no symptoms or any kind of distress and is not disturbed by the sight of the varicose veins, treatment might not be mandatory. However, if there are symptoms, treatment may be needed to relieve pain or discomfort, address the problem, such as leg ulcers, skin scarring, or swelling. Some patients prefer treatment for cosmetic purposes to get rid of the “ugly” varicose veins.
What changes in diet can help improve symptoms of Varicose Veins?
Losing weight can lower the pressure on your veins. Also, diet affects your veins. There are special foods that may reduce the risk of getting varicose veins.
- Watercress
- Foods High in Rutin
- Avocados
- Asparagus
- Beets
- Rosemary
Changes in lifestyle which can help Varicose Veins
Some of the recommended lifestyle changes to help prevent varicose veins from getting worsen. These approaches may also decrease discomfort and the risk of complications:
- Exercise regularly
- Elevate your legs
- Maintain healthy weight
- Avoid salts
- Wear compression garments
- Avoid tight dresses
- Avoid heels
Possible alternative remedies for Varicose Veins
You can try the following home remedies to help address the condition and improve symptoms:
- Extract of Plant – A research study suggests that horse chestnut extract, Aesculus hippocastanum L., may support reducing leg pain, heaviness, and itching in people with chronic venous undersupply, which is the main cause of varicose veins.
- Compression stockings are widely available, can help by applying pressure tthe legs. This helps the muscles and veins tpush blood toward the heart.
- Eating foods that contain flavonoids may alshelp a person tshrink their varicose veins.
- According the National Institute of Health Source, the use of grape seed extract, Vitis vinifera, orally may help to decrease swelling in the lower legs.