Information on this site shall be considered as holistic, alternative and spiritual advice only. For medical advice and treatment a GP, medical professional and/or Certified Hijama Therapist should be consulted. In all circumstances where lifestyle changes, supplements, or other foods are suggested your GP should be consulted. Client Safety is the number one priority.
Standard Wet Points – 1,55,11,12,13,34,35,36
Click here for Hijama Points on the back of the bodyClick here for Hijama Points on the head and face
Cupping / Hijama Treatment Plan for Quadriplegia
Allow 2-4 weeks between sessions – longer if required. Hijama Points shown for each session should ONLY be used to guide the therapist. Body size, cup size, and any other conditions need to considered and appropriate care and attention taken. The number of sessions shown can be increased or reduced depending on the condition of the client.
Complete Treatment Plan
Click here for Session 1Click here for Session 2
Click here for Session 3
Click here for Session 4
Click here for Session 5
Click here for Session 6
If the client has a complicated history and numerous concerns then it is a good idea to use our online consultation service – click here.
Which body part or function is involved in Quadriplegia?
The spinal cord is a bundle of nerves and cells that carry signals from the brain to the complete body. It is a long-extended nerve from the lower part of the brain to the lower back with varying lengths in each person. Some estimates report a length of spinal cord about 43 cm in females and 45 cm in males. The spinal cord is divided into three parts – the neck region is called cervical, the thoracic region is called the chest, and the part in the lower back is lumbar.
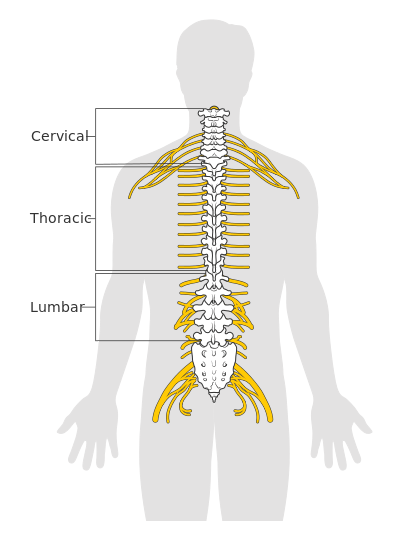
The spinal cord in the human body is well protected by three layers of tissue membranes including the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater and often these are called meninges. Moreover, the spinal cord and its meninges are further protected by the spinal bones or vertebral column starting from the base of the neck and extending to the lower back into the sacrum. The three regions of the spinal cord in the vertebral column are protected by different sets of spinal bones mostly 7 bones in the cervical column, 12 in the thoracic, and 5 in the lumbar. The cross-section of the spinal cord shows key regions including gray matter, white matter, posterior and anterior roots, spinal nerve, and spinal ganglions. The functions of the spinal cord include carrying signals from the brain to control body movement and autonomic functions. The spinal cord also transmits information like sensations of pain, pressure, and touch from the rest of the body back to the brain for processing. Also, it can conduct some motor reflexes independently of the brain like a jerk in the knee when tapped on a specific spot.
The spinal cord is a delicate body part susceptible to Injuries that can result in devastating body impairments. It can be damaged when a person suffers a sports-related injury, gunshot, or a vehicle accident. Any damage in the spinal cord can lead to permanent functional disability in a person as it plays a central role in body movement and sensation.
What are the symptoms and effects of Quadriplegia on the body?
Quadriplegia is also termed as tetraplegia leading to partial or total paralysis of all four limbs (both arms and legs) due to injury in the spinal cord, certain spinal cord diseases or a tumor can also cause the paralysis. There are several types of spinal cord injuries depending on the amount of damage it causes.
- Complete spinal cord injury:
When there is no sensation or motor function below the injury point and the nerves below this point can no longer send or receive signal to the brain it is termed as complete spinal cord injury, it is the most severe type of injury.
- Incomplete spinal cord injury:
When the motor function is lost below the injury point, but some nerve signals are still being sent and the patient has some sensation present.
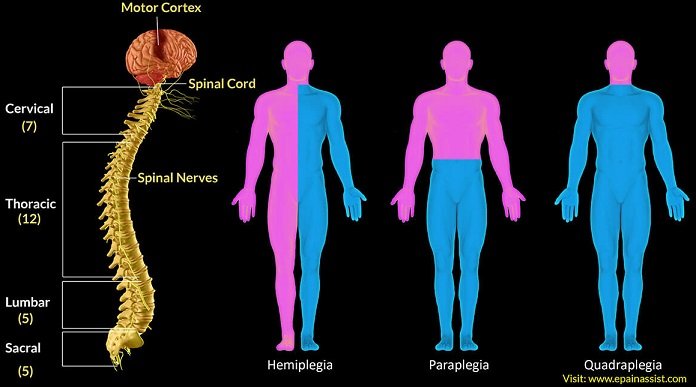
The most common symptom of the spinal injury is the impairment of the limb (arm or leg) and torso function. Due to these impairments control of various autonomic functions is also lost that include problem in breathing or coughing, digestion issues, a problem with sitting, spasms or extended reflexes, movement loss, loss of function of bowel and bladder, sensitivity loss, weakness in certain body areas, and sexual problems. Also, the loss of feeling in the area of damage causes numbness, sensitivity loss or neuropathic pain. Spinal cord injuries cause inactivity in a person that can cause other health problems including chronic pain, weak bones, pneumonia, infection of the urinary tract, sores, and muscle tightness.
The risk factors for spinal cord injuries leading to quadriplegia include:
- A family history of inherited nerve diseases
- History of cancer that can lead to suppression of spinal cord
- Medical complications
- The wound of a gunshot
Playing certain sports can increase the chances of spinal cord injury these may include gymnastics, football, ice hockey, wrestling, skiing, rugby, surfing, or diving.
What changes in diet can help improve symptoms of Quadriplegia?
Spinal cord injuries like quadriplegia lead to denervated muscles with reduced metabolic activity and require less than the normal number of calories in paralyzed person compared to normal individuals. It is recommended for the person with quadriplegia to take 23 calories per kg of weight and should be monitored regularly. Adding a variety of food with whole grains, proteins, fruits, and vegetables and avoiding food high in fat and calories is recommended in these patients.
Changes in lifestyle which can help Quadriplegia
Any type of physical activity consisting of appropriate exercises possible for the patient with spinal cord injury helps maintain weight and overall quality of life. The activity can be of any kind like swimming, wheelchair sports, exercises consisting of electric stimulation, or going out to the mall and practicing wheeling up and down with installed walkers in the mall.
Possible alternative remedies for Quadriplegia
The options for quadriplegia treatment other than surgical include language/speech therapy, physical therapy, occupational therapy, a muscle relaxant to control spasms, and resistance training, use of positioning devices, a walker, and a wheelchair.