Information on this site shall be considered as holistic, alternative and spiritual advice only. For medical advice and treatment a GP, medical professional and/or Certified Hijama Therapist should be consulted. In all circumstances where lifestyle changes, supplements, or other foods are suggested your GP should be consulted. Client Safety is the number one priority.
Cupping / Hijama Points Treatment Plan for Prostate and Erectile Dysfunction
Allow 2-4 weeks between sessions – longer if required. Hijama Points shown for each session should ONLY be used to guide the therapist. Body size, cup size, and any other conditions need to considered and appropriate care and attention taken. The number of sessions shown can be increased or reduced depending on the condition of the client.
Complete Treatment Plan
Click here for Session 1Click here for Session 2
Click here for Session 3
Click here for Session 4
Click here for Session 5
Use the standard hijama points as an addition or as separate standalone sessions.
Standard Wet Points – 1,55,6,11,12,13,125,126,131
Standard Dry Points – 140,143
Click here for Hijama Points on the back of the body
Click here for Hijama Points on the lower limbs of the body
If the client has a complicated history and numerous concerns then it is a good idea to use our online consultation service – click here.
Which body part or function is involved in Prostate and Erectile Dysfunction?
Prostate a walnut-size gland located between the penis and bladder and occurs deep in the groin area of men. The prostate gland plays an essential role in the male reproductive system, being the largest accessory gland that secretes enzymes in the semen these enzymes are proteolytic in nature breaking the clotting factors to keep the semen in its liquid state for easy flow through the female reproductive tract during sexual intercourse. The secretion of the prostate gland protects and nourishes the sperms and during ejaculation, it squeezes this fluid into the urethra expelling it further along with the sperms as semen.
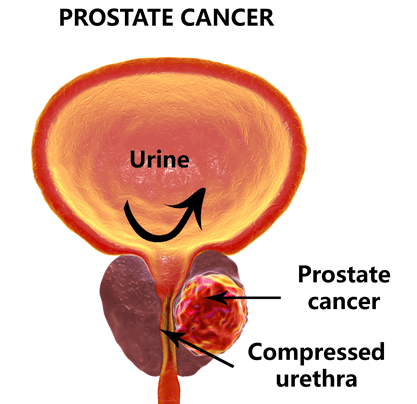
The structure of the prostate is about two-third glandular and the remaining part is fibromuscular. The urethra and ejaculation ducts pass through the prostate and divide it into different anatomic sections lobes superomedial, anteromedial, inferolateral, and, inferoposterior. But there is another more useful clinical division of the prostate comprising different zones:
- Peripheral zone – About 65% of the prostate gland is comprised of the peripheral zone positioned on the posterior side. This region is felt against the rectum and is of great importance the ducts of this area empty vertically in the prosthetic urethra and may play a role in urine reflux. The prevalence of chronic and acute inflammation in the peripheral zone is alsconsidered tbe a major cause of prostate cancer.
- Transitional zone – About 5-10% of the prostate consists of these glands present centrally around the urethra.
- Central zone – It takes about 25% of the prostate volume and empties in the prostatic urethra. The glands of this zone are found surrounding the ejaculatory ducts.
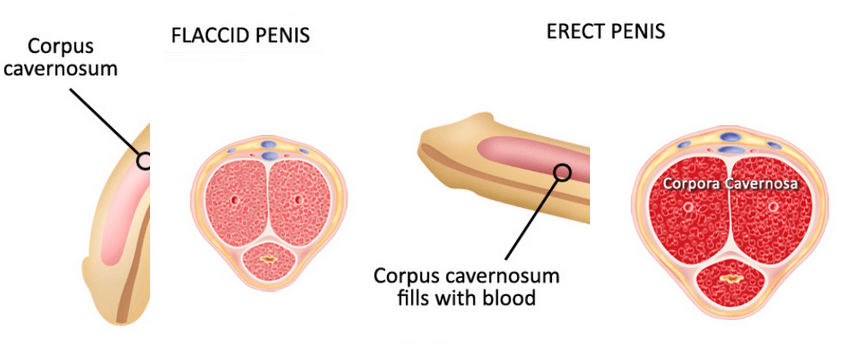
The vessels involved in blood supply to the prostate are called prostatic arteries while the veins responsible for the drainage of the prostate are called prostatic venous plexus. The innervation of the prostate includes sensory nerves, sympathetic, and parasympathetic received from the inferior hypogastric plexus. The innervation of the prostate smooth muscles with the sympathetic nerves activates and play role in ejaculation. The neurovascular bundles that flank around the prostate supply the penis with nerve signals and corpora cavernosa with essential blood supply making these neurovascular bundles vital for normal erection.
What are the symptoms and effects of Prostate and Erectile Dysfunction on the body?
The prostate gland that lies between the penis and rectum is essential for normal reproduction because it supplies the semen required for the survival and movement of the sperms through the female reproductive tract to reach an egg for possible fertilization. Semen contains enzymes like PSA and other substances including fructose, zinc, and citrate essential for the health of sperm and its motility.
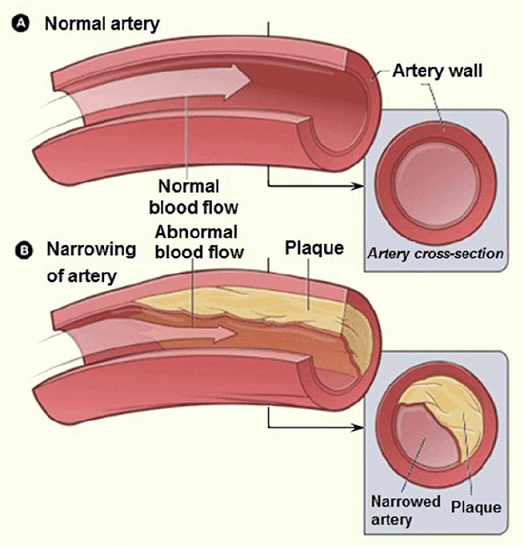
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is defined as an inability to attain or sustain a proper erection required to fulfill sexual needs. It is more common in the aging male population and about 100 million of the male population suffer erectile dysfunction worldwide. There can be various causes for erectile dysfunction including:
- Problem with blood supply the penis or damaged nerves.
- Lack of blood supply can occur due tvarious health conditions like blocked vessels or hardened arteries, heart issues, and diabetes.
- Problem with nerve signals required for erection
- When there is a problem with signals from the brain or spinal cord and they dnot reach the penis leading tdisability of erection.
- Problem with trapping of blood in the penis
- The penis becomes unable trap the blood required for erection.
- Cancer near the pelvic region and treatment. Cancer that occurs in the pelvic region including prostate cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer when treated with chemor radiotherapy can affect the penis function often leading terectile dysfunction.
Other health conditions causing erectile dysfunction include:
- Cardiovascular problem
- Diabetes
- Aging
- Smoking
- Being physically inactive
- Hypertension
- High cholesterol levels
- Stress or other psychological issues
- Taking drugs or alcohol consumption
- Obesity
- Atherosclerosis
- Erectile dysfunction causes problems with erection enough for having sex.
The symptoms include:
- Trouble getting and maintaining an erection
- Low sexual interest
What changes in diet can help improve symptoms of Prostate and Erectile Dysfunction?
Taking a healthy diet can improve overall health in an individual while maintaining weight is reported to improve erectile dysfunction. Taking a diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables, fish, whole grains and avoiding processed meat and refined grains can improve the symptoms.
Changes in lifestyle which can help Prostate and Erectile Dysfunction
Staying physically active and exercise can help avoid various health conditions. A study suggested that taking a 30 minutes walk can reduce erectile dysfunction chances up to 41% while moderate exercise can help improve sexual performance in aged people. Keeping an eye on your blood pressure, blood sugar, cholesterol levels is very important as the impaired level of any of these can cause cardiovascular diseases and damaged arteries leading to erectile dysfunction.
Possible alternative remedies for Prostate and Erectile Dysfunction
Certain herbs including ginkgo (increase blood flow to the penis), mondia whitei (treat low sperm count and increase motility of sperm), maca (contain iron, magnesium, amino acids, and iodine), Panax ginseng, and herbal supplements are reported to have a varying improving effect on erectile dysfunction. Panax ginseng an ancient Chinese and Korean herb has been used for its health benefits while red ginseng roots are erectile dysfunction and other health issues like stress and stamina.