Information on this site shall be considered as holistic, alternative and spiritual advice only. For medical advice and treatment a GP, medical professional and/or Certified Hijama Therapist should be consulted. In all circumstances where lifestyle changes, supplements, or other foods are suggested your GP should be consulted. Client Safety is the number one priority.
Cupping / Hijama Points Treatment Plan for Obesity
Allow 2-4 weeks between sessions – longer if required. Hijama Points shown for each session should ONLY be used to guide the therapist. Body size, cup size, and any other conditions need to considered and appropriate care and attention taken. The number of sessions shown can be increased or reduced depending on the condition of the client.
Complete Treatment Plan
Click here for Session 1Click here for Session 2
Click here for Session 3
Standard Wet Points – 1,55,9,10,120,49
Click here for Hijama Points on the front of the bodyClick here for Hijama Points on the back of the body
If the client has a complicated history and numerous concerns then it is a good idea to use our online consultation service – click here.
Which body part or function is involved in Obesity?
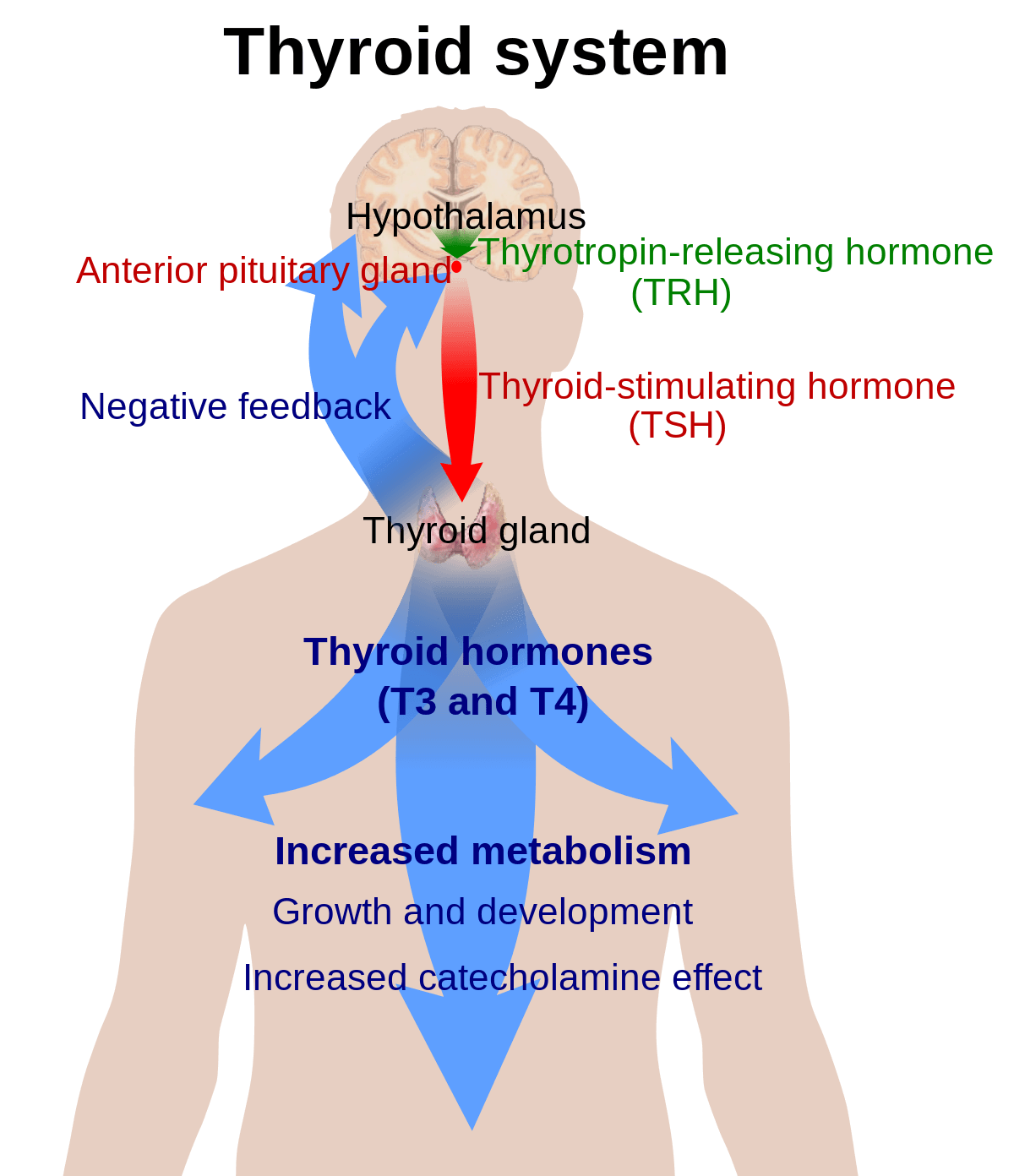
The thyroid gland is an important hormone-secreting gland and can be a vital component to obesity. It plays a vital role in the metabolism, growth, and developmental processes of the human body. It helps to supervise many body processes by continual secretion of a regular amount of thyroid hormones into the bloodstream. If the body requires more energy in specific functions for example, if it is maturing or cold, or during pregnancy, the thyroid gland release more hormones.
This glandular organ is placed at the anterior side of the neck, below the voice box. It is butterfly-shaped. The two side lobes of it pose against and around the trachea and are attached at the front by a narrow strip of muscle. It has been understood for a very long time that there is a problematic connection between thyroid disease, body weight, and metabolism. The thyroid hormone performs the metabolism process in humans. Metabolism is deduced by assessing the amount of oxygen used by the body over a certain amount of time. If the measurement is determined at rest, it is called the basal metabolic rate (BMR).
What are the symptoms and effects of Obesity on the body?
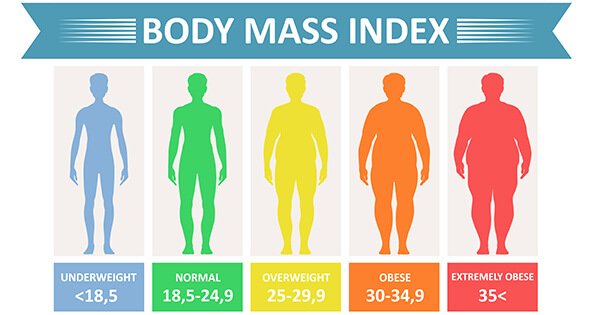
If a person is overweight or underweight is determined by their body mass index (BMI). We calculate the BMI of a person to find out either he/she is underweight or overweight. The body’s mass is divided by the square of the body height, expressed in kg/m² while resulting from mass in kilograms and height in meters. For adults, if BMI is between 25 to 30, they are considered overweight while beneath 18.5 is considered as underweight and between 18.5 to 25 normal.
The symptoms of obesity include:
- Joint pain: Pain in joints directly indicates obesity or overweight as your joints cannot bear excessive weight.
- Sleep Apnea: Difficulty in sleeping can also be a symptom of being overweight which leads to daytime drowsiness.
- Difficulty in breathing: An increase in fat can damage the respiratory system, increase pulmonary resistance, and decreased respiratory muscle strength.
- Skin Infections: The thick layers of subcutaneous fats due to obesity can cause skin infections and conditions which lead to skin diseases. Such as the obese persons sweat more than a normal person.
- Metabolic Imbalance: Obesity impacts metabolic activities because the higher body mass due to the fats increases the basal metabolic rate (BMR).
- High Blood Pressure – When someone gains weight to the level of obesity their kidneys become compressed physically and cause high blood pressure. The high amount of visceral and retroperitoneal fat around the kidneys is linked with hypertension, altered pressure natriuresis, and higher intrarenal pressure.
- Stroke – Being overweighed can increase the chances of getting a stroke. When an excess of fats is accumulated in the blood, poor blood flow and blockages are caused, due to which inflammation is likely to occur that leads to stroke.
- Type 2 Diabetes – Type 2 diabetes is called adult-onset diabetes and usually affects middle-aged or older people. It is more common in people who are overweight or obese due to impaired metabolism.
What factors increase the risk of Obesity?
Certain factor play role in a person’s being under or overweight including:
Age – When we measure a person’s BMI, age is always considered the primary factor because the body mass increases as with age. The children have low body mass, and adults have more body mass while older are normally weaker than adults and stronger than children. So, the measuring of BMI directly depends upon age.
Height – As with age, height is also an important factor, and mostly, the taller people weigh more than, the shorter ones. According to anatomical research, muscles are denser than fat, so taller people tend to have more muscles. That’s how height affects as an important factor in a person’s BMI. Genetics plays an important role in both of the factors mentioned above. Sometimes, a person weighs overweight or much taller; it may be due to genetics. We can’t declare these situations as a disease because genetics has a vital role in them. Being overweight or underweight both are abnormal conditions and are associated with many health problems.
Abnormally excessive accumulation of fat in the body causes health problems in a person. To classify an individual as underweight, overweight or obese their body mass index measurements are taken. The energy imbalance (calories intake and calories burned) is the most common cause of overweight or obesity. This can happen due to two common reasons:
- a person takes a higher amount of energy-dense food containing fats and sugars
- a person increasingly become physically inactive due to a sedentary lifestyle
Being overweight or obese is a gateway to many serious health conditions like cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and can become life-threatening if not treated at the right time.
What changes in diet can help improve symptoms of Obesity?
The standard and highly recommended dietary management for obesity are to avoid less healthy fatty foods and dairy products. It is also recommended to increase the proportion for lower energy-dense foods, fruits, and vegetables. Cutting the number of unhealthy fats from your daily routine is key to reducing weight.
Start simply making the right choices when you eat. Cut back and eventually remove any sugar form your diet; reduce carbs as much as possible; choose healthy fats whenever you can and stop eating fried foods; drop your portion sizes; starting eating fiber rich foods such as oats which will help to keep you feeling full for longer. Hijama for obesity can help improve your metabolism but without lifestyle changes you won’t get the long term health benefits that you’ll get by actually losing weight.
Changes in lifestyle which can help Obesity
Every overweight person should make some changes in their lifestyle to get rid of extra fat from the body. Start doing moderate exercises in a routine. According to most healthcare professionals, exercise is taking a great part in reducing weight, leading to diseases. Yoga, Swimming, Cycling, and daily walk are highly recommended for overweight people.
Possible alternative remedies for Obesity
Avoid smoking because it causes stiffness in fat muscles and increases stroke chances by forming clots in the blood and increasing your blood pressure. Secondly, follow a healthy diet plan with fewer fats, include vegetables and fruits, take healthy fresh juices and carbohydrates. Moreover, routine exercises also help improve weight and decrease the chances for serious life-threatening diseases.