Information on this site shall be considered as holistic, alternative and spiritual advice only. For medical advice and treatment a GP, medical professional and/or Certified Hijama Therapist should be consulted. In all circumstances where lifestyle changes, supplements, or other foods are suggested your GP should be consulted. Client Safety is the number one priority.
Hijama / Cupping Points Treatment Plan for Hemorrhage (vaginal bleeding)
Allow 2-4 weeks between sessions – longer if required. Hijama Points shown for each session should ONLY be used to guide the therapist. Body size, cup size, and any other conditions need to considered and appropriate care and attention taken. The number of sessions shown can be increased or reduced depending on the condition of the client.
Complete Treatment Plan
Click here for Session 1Click here for Session 2
Click here for Session 3
Click here for Session 4
Use the standard hijama points as an additional or as separate standalone sessions.
Standard Wet Points – 1,55
Click here for Hijama Points on the back of the bodyIf the client has a complicated history and numerous concerns then it is a good idea to use our online consultation service – click here.
Which body part or function is involved in Hemorrhage (vaginal bleeding)?
Normal vaginal bleeding, or menstruation (also called a period), is part of a woman’s menstrual cycle. It typically occurs every 21 to 35 days and lasts from two to seven days. Abnormal vaginal bleeding or hemorrhage is bleeding from the vagina that appears:
- During periods
- After intercourse
- Between menstruation, but is heavier than normal or that lasts more than common or more than seven days
- Postmenopause
Causes
Hemorrhage in the vagina has various causes, such as fibroids, endometrial polyps, uterus infection, pregnancy, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, kept products of conception after pregnancy, or tumor in the uterus, endometrial and cervical cancers. A lot of women experience abnormal bleeding between their menstruation at some point in their lives. Hemorrhage in the vagina occurs when you have:
- Bulkier bleeding than usual
- Bleeding lasting for more than 7 days
- Spotting or bleeding during periods
- Bleeding after intercourse
- Bleeding after menopause
- Bleeding During pregnancy
- Bleeding before age of puberty
- Menstrual cycles extended till 35 days or less than 21 days
- Absent period for 3 to 6 months (amenorrhea)
Massive bleeding during the first few weeks after delivery (postpartum) or after an abortion is normal because the uterus has not contracted to the pre-pregnancy size or because fetal tissue resides in the uterus.
At age 40 or older, vaginal hemorrhage may suggest that you are entering the perimenopause stage. In a woman who is going through menopause, and has not had to bleed for 12 months, vaginal bleeding is always abnormal and should be discussed with your doctor. Hemorrhage can be explained in various terms, such as vaginal bleeding after menopause and oligomenorrhea.
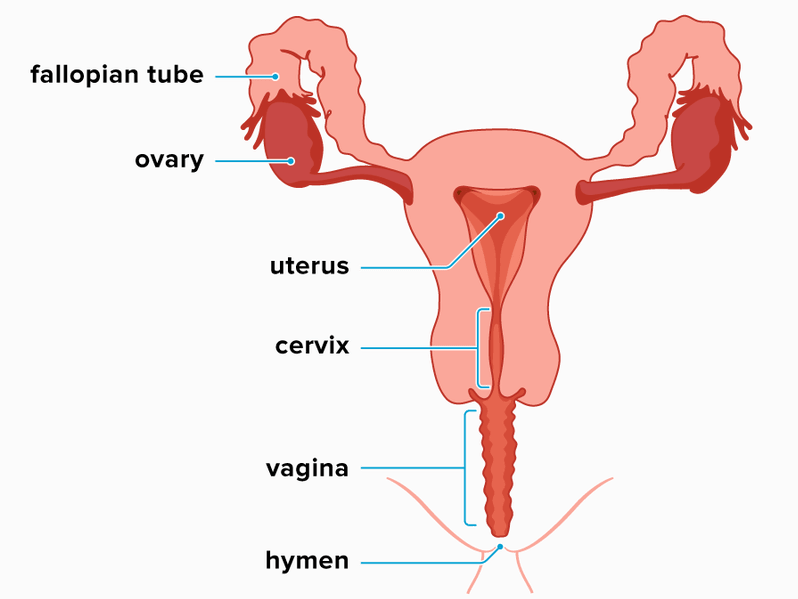
The terms related to vaginal bleeding include:
- Blood in vaginal discharge
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
- Menorrhagia
- Menstrual bleeding
- Oligomenorrhea
- Polymenorrhea
- Spotting
- Vaginal bleeding after sex
What are the symptoms and effects of Hemorrhage (vaginal bleeding) on the body?
There are many causes of hemorrhage (vaginal bleeding). Abnormal vaginal bleeding is always related to abnormal or failure of ovulation (anovulation). Doctors call the problem abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) or ovulatory uterine bleeding. AUB is more familiar in teenagers and in women who are close to menopause.
Women who take oral birth control may undergo events of abnormal vaginal bleeding. Primarily this is called “breakthrough bleeding.” This problem sometimes goes away by itself. Still, talk to your health care specialist if you have problems with the bleeding.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy problems such as:
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Threatened miscarriage
Problems with reproductive organs
Complications with reproductive organs may include:
- Uterus infection (pelvic inflammatory disease)
- Fresh injury or surgery to the uterus
- Noncancerous developments in the uterus, including uterine fibroids, uterine or cervical polyps, and adenomyosis
- Infection in the cervix (cervicitis)
- Injury or disorder of the vaginal entrance (caused by sex, infection, polyp, genital warts, ulcer, or varicose veins)
- Endometrial hyperplasia (thickening or build-up of the wall of the uterus)
Medical Conditions
Difficulties with medical conditions may include:
Polycystic ovary syndrome(PCOS)
- Cancer or tumor of the cervix, uterus, ovary, or fallopian tube
- Thyroid or pituitary gland disorders
- Diabetes
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Lupus erythematosus
- Bleeding disorders
Symptoms
A flow of blood exceeding out from the vagina that occurs at an irregular time during the month or in inappropriate amounts. Make notes of when your periods start and end, the massiveness and duration of your bleeding, and when and how much you bleed during periods The signs of abnormal uterine bleeding include:
- Heavy bleeding (menorrhagia) during your periods
- Bleeding after periods, after sex, or during menopause
- Lasting periods (more than 7 days)
- Abnormal periods
- Vaginal itching
- Vaginal discharge
- Vaginal dryness
- very low blood pressure.
- Increased heart rate.
- sweaty, wet skin that frequently feels cool to the touch.
- Pain
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Fever
What changes in diet can help improve symptoms of Hemorrhage (vaginal bleeding)?
Take a balanced diet that is rich in iron and vitamin C. Foods enriched with iron are red meat, shellfish, eggs, beans, and leafy green vegetables. Bright vegetables such as bell peppers, pumpkin, carrots, artichokes, and purple cabbage are full sources of antioxidants and must be present in your diet.
Changes in lifestyle which can help Hemorrhage (vaginal bleeding)
Hemorrhage can be cured if we know the cause, whereas irregular bleeding can be improved by some changes in diet, exercise along with prescribed medication by a consultant. Ovulatory dysfunction can also be treated through lifestyle improvement in women with adiposity, PCOS, or other circumstances in which ovulatory cycles are inferred. Try warm pads, Wear period panties to bed, Get a lot of rest and practice Exercise and yoga.
Possible alternative remedies for Hemorrhage (vaginal bleeding)
There are no remedies for uterine hemorrhage, but urgent consultation is recommended.