Information on this site shall be considered as holistic, alternative and spiritual advice only. For medical advice and treatment a GP, medical professional and/or Certified Hijama Therapist should be consulted. In all circumstances where lifestyle changes, supplements, or other foods are suggested your GP should be consulted. Client Safety is the number one priority.
Cupping / Hijama Points Treatment Plan for Diabetes Type 2
Allow 2-4 weeks between sessions – longer if required. Hijama Points shown for each session should ONLY be used to guide the therapist. Body size, cup size, and any other conditions need to considered and appropriate care and attention taken. The number of sessions shown can be increased or reduced depending on the condition of the client.
Complete Treatment Plan
Click here for Session 1Click here for Session 2
Click here for Session 3
Click here for Session 4
Use the standard hijama points as an additional or as separate standalone sessions.
Standard Wet Points – 1,55,6,7,8,22,23,24,25,120,49
Click here for Hijama Points on the front of the bodyClick here for Hijama Points on the back of the body
If the client has a complicated history and numerous concerns then it is a good idea to use our online consultation service – click here.
Which body part or function is involved in Diabetes Type 2?
Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic syndrome associated with increased plasma glucose level and disruption in glucose metabolism. In the human body, there is an organ pancreas which is located behind the liver and the stomach. Apart from producing digestive enzymes, the pancreas also produces hormones such as glucagon and insulin into the bloodstream to regulate the glucose levels of the body. Insulin and glucagon work in an opposite manner to each other for the regulation of blood glucose level. When the sugar level is high in the blood, it sends a signal to the beta cells of the pancreas and insulin is secreted by the pancreas into the bloodstream. Consequently, it lowers the blood glucose levels by allowing the cells to uptake the glucose from the blood. When the blood sugar level is low, the pancreas releases glucagon into the blood which stimulates the liver to release glucose from glycogen breakdown.
Despite best control attempts high blood sugar for a prolonged period leads to long-term complications like nephropathy, neuropathy, and retinopathy. Nephropathy results due to high blood sugars and high blood pressure. Therefore, routine check-up of blood sugar and pressure is essential, the patient should consult the physicians to keep sugar level under control and avoid further complications. Neuropathy is manifested by numbness in feet, cracks or breakdown of skin tissues, calluses, and redness. Retinopathy can be diagnosed earlier if a patient goes for a regular eye examination, blurred vision and blind spots should be taken seriously to avoid further loss. Other complications include cataracts, glaucoma, dental issues, stroke, and heart attacks.

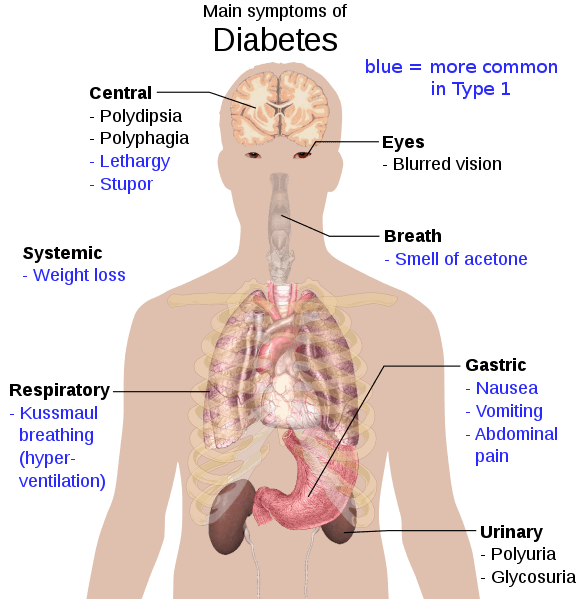
What are the symptoms and effects of Diabetes Type 2 on the body?
The incidence of diabetes mellitus is increasing globally. According to the 2019 statistics of the International Diabetes Federation, the prevalence of diabetes is 9.3% and is predicted to be 10.2% by 2030, and 10.9% by 2045. Diabetes is more prevalent in urban areas.
Based on the underlying mechanism of the disorder, the types of diabetes are Type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Symptoms, diagnosis, and management also vary with the type of diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 diabetes is the manifestation of an autoimmune disorder, in which the immune system starts to attack the body’s cells. This type of diabetes is caused when the immune system attack on Beta cells of the pancreas and destroy them. Genetics and viral infections are considered to be responsible for the autoimmune attack. Type 1 diabetes prevalence is low as only 5% of diabetic patients develop this type. Symptoms include fatigue, extreme thirst and hunger, frequent urination, blurry vision, and unintentional weight loss. As in type 1 diabetes, the body is unable to produce insulin, such patients need insulin supply through pumps or injections.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
It is the most common form of diabetes. It is caused by a combination of many environmental and genetic factors which affect the ability of pancreatic beta cells to produce insulin and tissue sensitivity to insulin (liver, muscle, adipose and pancreas). In this type, either pancreatic insulin production is not sufficient or body cells develop resistance to it. It often starts with insulin resistance, as the condition persists pancreatic insulin production is gradually lost. Genetics, environmental factors, lifestyle, and obesity are underlying causes. Symptoms include sores that heal slowly, increased urination, hunger, and thirst, blurry vision. Type 2 diabetes can be managed by maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Gestational Diabetes
This type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy in overweight women and those who gain excessive weight during pregnancy are also at risk to develop this condition. During pregnancy placenta produce hormones which make cells of the pregnant women less sensitive to effects of insulin, resulting in high blood glucose level. Women with gestational diabetes usually do not experience any symptoms, and it is diagnosed during routine blood glucose test in the 24th and 28th week of gestation. Rarely, women with gestational diabetes experience increase thirst and urination.
What changes in diet can help improve symptoms of Diabetes Type 2?
Diet plays an important role in controlling diabetes and avoiding its complexities. A diabetic person should eat healthy items from each food group in a balanced manner. Vegetables like broccoli, carrots, peas, corn, potatoes. Fruits like melons, berries, apples, and bananas. Low-fat dairy products like yogurt. Protein in the form of lean meat, dried beans and chickpeas. Tofu as a meat substitute. They should avoid fried foods with high trans and saturated fat, food items with high salt, sweetened beverages and drinks.
Changes in lifestyle which can help Diabetes Type 2
Complexities of diabetes can be prevented and controlled by adopting a healthy lifestyle. A healthy balanced diet and physical activity are the main factors of a healthy lifestyle. Being physically active helps the person to maintain the blood glucose level, cholesterol and blood pressure in the target range. Regular exercise is also effective in reducing stress as stress increases blood sugar levels. Keeping the record of blood glucose level, balance diet with proper knowledge of the right proportion of each food group, physical activity, regular consultation with a physician, avoiding smoking, alcoholic and carbonated drinks help the person to remain healthy and delay or prevent diabetes-associated complexities.
Possible alternative remedies for Diabetes Type 2
Besides insulin injections and medicines, people with diabetes often opt for complementary and alternative medicines (CAM). CAM has been the focus of research for many years and their use is increasing. CAM includes medicinal herbs such as garlic, neem, bitter lemon, and fenugreek among many others. FDA does not consider these herbs as medicines. Dietary supplements such as nicotinamide, vitamin E, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, physical interventions such as yoga, aromatherapy, acupuncture, and chromotherapy.