Information on this site shall be considered as holistic, alternative and spiritual advice only. For medical advice and treatment a GP, medical professional and/or Certified Hijama Therapist should be consulted. In all circumstances where lifestyle changes, supplements, or other foods are suggested your GP should be consulted. Client Safety is the number one priority.
Cupping / Hijama Points Treatment Plan for Atrophy of Brain Cells
Allow 2-4 weeks between sessions – longer if required. Hijama Points shown for each session should ONLY be used to guide the therapist. Body size, cup size, and any other conditions need to considered and appropriate care and attention taken. The number of sessions shown can be increased or reduced depending on the condition of the client.
Complete Treatment Plan
Click here for Session 1Click here for Session 2
Click here for Session 3
Click here for Session 4
Use the standard hijama points as an additional or as separate standalone sessions.
Standard Wet Points – 1,55,101,36,32,34,35,11,44,43
Click here for Hijama Points on the back of the bodyClick here for Hijama Points on the head and face
If the client has a complicated history and numerous concerns then it is a good idea to use our online consultation service – click here.
Which body part or function is involved in Atrophy of Brain Cells?
The brain is one of the largest vital organs and most complex in its structure in the human body. It is composed of more than 100 billion nerves that transmit in numerous connections called synapses. The brain is made up of many proficient structures that work together:
The cortex is the outermost part of the brain. Thinking and voluntary movements initiate in the cortex. The brain stem extends from the spinal cord to the rest of the brain. Essential processes like breathing and sleep are regulated by this. The basal ganglia are a collection of structures in the middle of the brain. The basal ganglia coordinate information between many other brain structures. The cerebellum is present at the base and the posterior side of the brain. The cerebellum is dependable for coordination and balance. Because of the delicacy of the brain and spinal cord, the human body has a built-in defense system against injury.
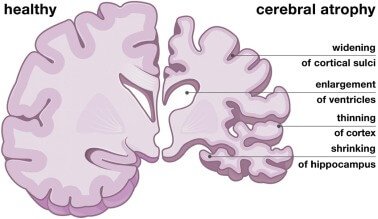
The skull and the meninges the lining of the brain secure the brain, while the bones of the spinal column protect the spinal cord, and cerebrospinal fluid surrounds and supports both the brain and the spinal cord. Atrophy of any tissue means damage to cells. In brain tissue, atrophy depicts a loss of neurons and the communication between them. Atrophy can be generalized, referred to as the shrinking of all the brain cells; or it can be focal, involving only a particular area of the brain and raising a drop of the functions that area of the brain regulates. If the cerebral hemispheres (the two lobes of the brain that form the cerebrum) are under effect, receptive thought and voluntary actions may be distorted. Atrophy can affect several structures of the brain. Based on the underlying cause, cerebral atrophy may improve very gradually or very rapidly.

What are the symptoms and effects of Atrophy of Brain Cells on the body?
Brain atrophy is a cerebral dysfunction that results in a significant loss of brain cells called neurons. Atrophy also demolishes the connections that help the cells linked together. It can be caused by different diseases that defect the brain, including stroke and Alzheimer’s disease. The destruction of brain cells is a natural process that occurs as hon get old, but this is a slow process. Brain atrophy related to any disease or injury occurs more quickly and is more damaging. Cerebral atrophy is a regular attribute of various disorders that affect the brain.
Focal atrophy involves cells in specific areas of the brain and results in loss of function in those specific brain areas. Generalized atrophy involves cells of all parts of the brain. Survival hope among patients with brain atrophy depends on the condition that is induced. A person with Alzheimer’s disease lives a standard period of four to eight years after their diagnosis. People with multiple sclerosis can have near to a normal life duration if they are treated effectively. Cerebral atrophy is a fatal condition, and there is no cure for it. Treatment for cerebral atrophy directs on treating the symptoms and difficulties of the disease.
Brain atrophy can involve one or many areas of the brain. The symptoms of brain atrophy may differ, depending on which part or parts of the brain are affected.
1. Dementia – The is characterized by the loss of memory, learning, conceptual thinking, and managerial functions such as planning and organizing. symptoms connected with a progressive decrease in brain function.
2. Seizures – A seizure is an immediate, unusual spike of electrical activity in the brain. There are two major types of seizure. The partial seizure, which involves just one region of the brain. The other is the generalized seizure, which involves both sides of the brain.
The symptoms of a seizure base on which portion of the brain it impacts on. Some people may not undergo any visible symptoms, whereas others may have a part in one or more of the following:
- behavioral changes
- tugging eye movements
- a bitter taste in the mouth
- dribbling or frothing at the mouth
- teeth clenching
Aphasias – The term indicates to a group of symptoms that simulate a person’s communicating abilities. Some types of aphasia can defect a person’s ability to make or understand speech. Stroke occurs when blood flow to part of the brain is suspended. Missing a supply of oxygen-rich blood, neurons in the area start destruction. Traumatic brain injury is injury to the brain that may be induced by a fall, motor vehicle accident, or any hit to the head.
Causes: Serious cases of cerebral atrophy have a long list of causes, virtually any source of brain-cell death. These can be classified extensively as diseases, infections, or injuries.
Following are examples:
- Cerebral palsy
- Dementias, including Alzheimer’s disease
- Huntington’s disease
- Leukodystrophies
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Parkinson’s disease
- Pick’s disease
What changes in diet can help improve symptoms of Atrophy of Brain Cells?
The foods we intake have a big effect on the structures and health of our brains. Eating a brain-boosting diet can aid both short- and long-term brain function, also reduce the atrophy of brain cells as you age.
- Oily fish
- Dark Chocolate
- Berries
- Nuts and seeds
- Whole grain
- Coffee
- Avocados
Changes in lifestyle which can help Atrophy of Brain Cells
There are numerous ways to delay atrophy, managing blood pressure, eating a healthy diet, exercising, staying physically active mentally and socially, and supplements. It’s important as well to drink alcohol poorly and prevent smoking.
Although a healthy diet is anyhow suggested, it’s almost impossible to attain every day. Supplementing with a product enclosing guarana seed extract can help incredibly to increase focus and sharpen memory.
Possible alternative remedies for Atrophy of Brain Cells
According to the research moderate exercise such as gardening and even dancing can help to delay brain shrinkage. In their study, the researchers said people who used to have a moderate or high level of exercise per week had brains that had the equal of 4 fewer years of brain aging.