Information on this site shall be considered as holistic, alternative and spiritual advice only. For medical advice and treatment a GP, medical professional and/or Certified Hijama Therapist should be consulted. In all circumstances where lifestyle changes, supplements, or other foods are suggested your GP should be consulted. Client Safety is the number one priority.
Cupping / Hijama Points Treatment Plan for Epilepsy
Allow 2-4 weeks between sessions – longer if required. Hijama Points shown for each session should ONLY be used to guide the therapist. Body size, cup size, and any other conditions need to considered and appropriate care and attention taken. The number of sessions shown can be increased or reduced depending on the condition of the client.
Complete Treatment Plan
Click here for Session 1Click here for Session 2
Click here for Session 3
Click here for Session 4
Use the standard hijama points as an additional or as separate standalone sessions.
Standard Wet Points – 1,55,101,36,32,107,114,11,12,13
Click here for Hijama Points on the back of the bodyIf the client has a complicated history and numerous concerns then it is a good idea to use our online consultation service – click here.
Which body part or function is involved in Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a disorder that affects the brain. Specifically, it is caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. This abnormal activity can be caused by a variety of factors, such as brain injury, infection, genetic predisposition, and developmental disorders, and it can lead to a variety of symptoms such as seizures, convulsions, muscle spasms, loss of consciousness, and changes in behavior or sensation. The brain’s electrical activity is regulated by a network of nerve cells called neurons which communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals. In epilepsy, these signals become disrupted, leading to the seizures and other symptoms associated with the disorder.
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurring seizures. The exact cause of epilepsy is often unknown, but it can be caused by a variety of factors, including brain injury, infection, genetic predisposition, and developmental disorders. Treatment options for epilepsy include medication, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
What are the symptoms and effects of Epilepsy on the body?
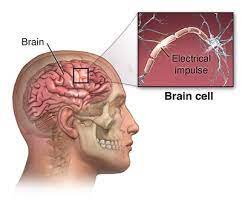
The symptoms and effects of epilepsy can vary depending on the type of seizures a person experiences and the part of the brain affected by the abnormal electrical activity.
Common symptoms
- Convulsions or muscle spasms
- Loss of consciousness or staring spells
- Sudden muscle contractions, such as arm or leg twitching
- Changes in behavior or sensation such as confusion, fear, or deja vu
- Uncontrolled movements such as jerking or staring
Long-term Effects
- Difficulty with memory, concentration and learning
- Depression or anxiety
- Difficulty with employment and social interactions
- Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP)
Additionally, seizures can also cause physical injury, such as falls or accidents, especially if the person loses consciousness during a seizure.
It’s important to note that not all seizures are caused by epilepsy, and it is important to seek medical evaluation if you experience any of these symptoms in order to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
What changes in diet can help improve symptoms of Epilepsy?
Ketogenic Diet
A high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that has been shown to be effective in reducing seizures in some people with epilepsy, particularly in children. The diet forces the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrates, which produces a metabolic state called ketosis that can have an anticonvulsant effect.
Modified Atkins diet (MAD)
Is also low in carbohydrates, but unlike the ketogenic diet, it doesn’t require precise measurements of fat and protein.
Additionally, avoiding foods that are high in sugar and refined carbohydrates may also be beneficial for people with epilepsy. Some studies have suggested that a low-glycemic-index diet, which emphasizes foods that have a lower impact on blood sugar levels, may help to reduce seizures in some people with epilepsy.
It is important to note that these diets should only be followed under the guidance of a physician and/or dietitian, as they may not be suitable for everyone and can have adverse effects if not properly managed.
While dietary changes may be beneficial for some people with epilepsy, it is not a substitute for traditional medical treatment and the best course of action would be to work with your healthcare provider to create a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs.
Changes in lifestyle which can help Epilepsy
In addition to medication and dietary changes, there are several lifestyle changes that can help to improve symptoms of epilepsy. These include:
- Getting enough sleep: Sleep deprivation can increase the likelihood of seizures, so it’s important to stick to a regular sleep schedule and get at least 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
- Avoiding triggers: Some people with epilepsy have specific triggers that can increase the likelihood of seizures. These may include stress, alcohol, caffeine, and certain medications. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help to reduce the frequency of seizures.
- Regular exercise: Regular physical activity can improve overall health and reduce the likelihood of seizures. However, it is important to speak with your doctor about the appropriate type and intensity of exercise, as some activities may be too strenuous for some individuals.
- Managing stress: Stress can be a trigger for seizures, so it’s important to find ways to manage stress and relax, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Avoiding risky activities: Some activities, such as swimming or climbing, can be dangerous for people with epilepsy because of the risk of injury during a seizure.
- Taking medications as prescribed: It’s important to take medications as prescribed and to follow-up with the healthcare provider regularly to evaluate the effectiveness and any side effects of the medication.
It’s important to note that lifestyle changes should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider to ensure they are appropriate and safe for the individual.
Possible alternative remedies for Epilepsy
There are a number of alternative remedies that some people with epilepsy may find helpful in managing their symptoms. However, it’s important to note that these remedies have not been extensively studied and may not be effective for everyone. It’s also important to speak with a healthcare professional before trying any alternative remedies, as they may interact with other medications or have other risks.
- Herbal supplements: Some herbal supplements, such as valerian root, passionflower, and kava kava, have been found to have sedative and anti-anxiety effects and may be helpful in reducing seizures.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. Some studies have found that acupuncture may be effective in reducing seizures in some people with epilepsy.
- Massage therapy: Massage therapy has been found to help reduce stress and tension, which can be triggers for seizures in some people with epilepsy.
- Yoga and meditation: Yoga and meditation are mind-body practices that can help to reduce stress and improve overall well-being, which can be beneficial for people with epilepsy.
- Chiropractic care: Chiropractic care is a complementary therapy that involves the manipulation of the spine and other joints to improve overall health. Some people with epilepsy may find that chiropractic care can help to reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
It’s important to note that these alternative remedies should not replace traditional medical treatment, and the best course of action would be to work with your healthcare provider to create a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs.