Information on this site shall be considered as holistic, alternative and spiritual advice only. For medical advice and treatment a GP, medical professional and/or Certified Hijama Therapist should be consulted. In all circumstances where lifestyle changes, supplements, or other foods are suggested your GP should be consulted. Client Safety is the number one priority.
Hijama / Cupping Points Treatment Plan for Food Allergies
Allow 2-4 weeks between sessions – longer if required. Hijama Points shown for each session should ONLY be used to guide the therapist. Body size, cup size, and any other conditions need to considered and appropriate care and attention taken. The number of sessions shown can be increased or reduced depending on the condition of the client.
Complete Treatment Plan
Click here for Session 1Click here for Session 2
Click here for Session 3
Click here for Session 4
Click here for Session 5
Click here for Session 6
If the client has a complicated history and numerous concerns then it is a good idea to use our online consultation service – click here.
Which body part or function is involved in Food Allergies?
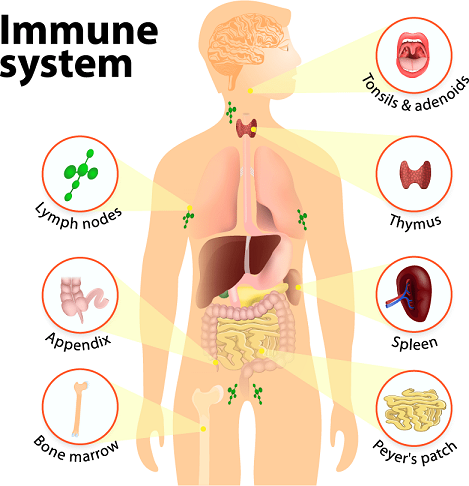
The immune system is the most essential component of the body for survival without which human survival is impossible due to the pathogen (viruses, bacteria, and parasites) present in the environment. The immune system is composed of multiple tissues, organs, cells, proteins, and chemicals that are spread throughout the body. The components of this system are specialized to distinguish the self from non-self-components and dead and faulty cells to remove them from the system without harming the body. When the immune system encounters any pathogen, it starts a cascade of reactions that leads to an immune response.
The immune system in the human body remains in a constant fight with some common infections like seasonal flu and cold that are caused by multiple strains of different viruses. The immunity against one virus does not protect a person from getting infected by another virus that is infecting for the first time, so this battle keeps going as our body gets exposed to new pathogens. The major components of the immune system include:
- Lymphatic system
- Spleen
- Thymus
- Antibody
- Bone marrow
- White blood cells
- Antibodies
Besides this, various other barriers protect our body from the attack of pathogens leaving no loophole in the body’s defense these include:
Skin: act as a barrier against the direct pathogens that are in continuous contact with our skin surface by secreting oils with antimicrobial properties.
Lungs: lungs are lined with mucous-producing cells the mucous efficiently traps the foreign particles and cilia pushes the mucous towards the mouth to cough it out.
Digestive tract: also have a mucous lining having antibodies and also the stomach acids are efficient in killing the pathogens.
Other than that, saliva and tears also contain antibacterial enzymes eliminating the chances of infection. When there is some impairment in any of the immune components our body is exposed to the harmful pathogens leading to infections and other health problems. Food allergy is also an immune system reaction that arises immediately after the intake of a certain food. Even a small amount of the allergy-causing food can cause signs and symptoms such as digestion issues and bulged airways. In some cases, a food allergy can cause drastic symptoms or even a lethal reaction referred to as anaphylaxis.
What are the symptoms and effects of Food Allergies on the body?
Food allergy affects approximately 6 to 8 percent of children under age 3 and up to 3 percent of adults. As there’s no cure for it, some children outgrow their food allergy as they grow older. It’s easy to mystify a food allergy with a much more common condition known as food tolerance. While annoying, food intolerance is a serious condition that does not involve the immune system.
To protect you from any bacterial infections nature has developed a perfect mechanism that is called the immune system. The body’s immune system resists foreign particles by fighting off bacteria and other infectious agents to maintain your good health. A food allergy reaction occurs when your immune system overreacts to a food or food particle, observing it as a danger and triggering a defensive response. While allergies tend to run in inheritance, it is difficult to predict whether a child will inherit a parent’s food allergy or whether siblings will have similar food allergies. Some research does suggest that if a child is experiencing allergies to some foods then his younger sibling will be allergic to the same food. People allergic to a particular food may also have a reaction to a similar food.
A food allergy will usually cause some kind of reaction every time the person interacts with trigger food. While food allergies may develop at any age. If you observe a food allergy, it is advised to see an allergist. Symptoms of a food allergy can vary from moderate to severe. Just because an initial reaction causes little issue doesn’t mean all reactions will be similar; a food that caused only mild symptoms on the first experience may cause more severe symptoms at another time.
Most food-related symptoms occur within two hours of intake; often they start immediately. In some very unusual cases, the reaction may be limited by four to six hours or even longer. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include the skin, the digestive system, the circulatory system, and the respiratory tract. They can arise in the following ways:
- Dyspnea
- Wheezing
- Cough
- Circulatory collapse
- Swelling of tongue
- Vomiting
- Dizziness or feeling faint
- Hives
- Anaphylaxis
- Weak pulse
- Pale or blue coloration of the skin
- Stomachache
When your body’s immune system gets alert about any foreign activity it produces an antibody to protect your body from any infection. Antibodies identify threats to your body, such as bacteria and viruses. They signal your immune system to release chemicals to execute the threat and prohibit the spread of infection.
Allergies are triggered when antibodies mistakenly target certain proteins present in your food. And release chemicals that result in the reaction. A type of food allergy called a non-IgE-mediated food allergy, caused by varied cells in the immune system. This type of reaction is largely shown to the skin and digestive tract, causing symptoms such as acidity, heartburn, indigestion and eczema. In children, the foods that mostly cause an allergic reaction are: * Eggs * milk * soya * wheat * peanuts. In adults, the foods that mostly cause an allergic reaction include peanuts, tree nuts, walnuts, brazil nuts, almonds and pistachios fish shellfish such as crab, lobster, celery, gluten, mustard, sesame seed, pine nuts, meat.

What changes in diet can help improve symptoms of Food Allergies?
Eating a healthy diet full of fruits and vegetables can be helpful in preventing allergies. Probiotics have been proven to contain both anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic properties, Spicy foods and with a little kick can help prevent food allergy, Vitamin C also beneficial, bioflavonoids and Magnesium-rich foods are proven to prevent an allergic reaction.
Changes in lifestyle which can help Food Allergies
Some of the guidelines are very important for a healthy lifestyle and to prevent yourself from food poison:
- Wash your hands properly
- Wash your cooking equipment
- Use a separate chopping board
- Separate raw meat
- Temperature of your fridge should be maintained below 5C
- Cool thoroughly
Possible alternative remedies for Food Allergies
Underlying some remedies that can help in allergies.
- Apple cider vinegar
- Balance it with banana
- Use of cumin
- Use of ginger and garlic
- Use of herbal teas
- Initiate detox diet
- Use of basil
- Yogurt with fenugreek seeds