Information on this site shall be considered as holistic, alternative and spiritual advice only. For medical advice and treatment a GP, medical professional and/or Certified Hijama Therapist should be consulted. In all circumstances where lifestyle changes, supplements, or other foods are suggested your GP should be consulted. Client Safety is the number one priority.
Complete Hijama Treatment Plan for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Allow 2-4 weeks between sessions – longer if required. Hijama Points shown for each session should ONLY be used to guide the therapist. Body size, cup size, and any other conditions need to considered and appropriate care and attention taken. The number of sessions shown can be increased or reduced depending on the condition of the client.
Complete Treatment Plan
Click here for Session 1Click here for Session 2
Click here for Session 3
Click here for Session 4
Click here for Session 5
Click here for Session 6
Standard Wet Points – 1,55,120,49,36
Click here for Hijama Points on the front of the bodyClick here for Hijama Points on the back of the body
Click here for Hijama Points on the head and face
If the client has a complicated history and numerous concerns then it is a good idea to use our online consultation service – click here.
Which body part or function is involved in Rheumatoid Arthritis?
The immune system protects a person from harmful foreign invaders (bacteria, viruses, and other toxins), and takes swift action by producing antibodies against these foreign particles. But in rare cases, the immune system can mistake its body cells as foreign invaders and start producing antibodies against them leading to different autoimmune disorders.
Autoimmune disorders are mostly prolonged, and treatment often involves easing the symptoms and slowing down the disease progression. Both genetic, as well as environmental factors, can cause these disorders. Like there are higher chances of patients developing rheumatoid arthritis when a gene named HLA-DR4 is present in them. On the other hand, environmental factors like viral infections and smoking can trigger and increase the chances of developing an autoimmune disease. Frequently both genetic makeup and environmental exposure act together to cause such malfunctions in the immune system.
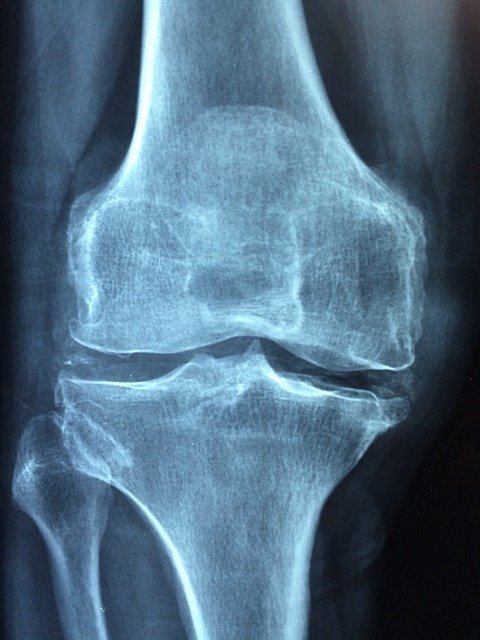
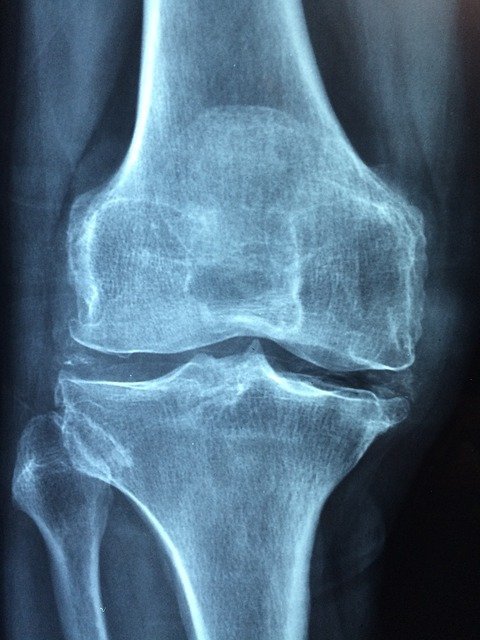
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune, systemic inflammatory disease caused when immune system generated antibodies get attached with the lining of synovial joints (both small and large joints) and immune cells mistakenly start to attack the joints triggering widespread inflammation, swelling, and pain.
Immune cells including B-cells and macrophages play a crucial role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by either residing in the synovium or circulating in the peripheral blood. The B-cells also secrete important physiologic proteins including rheumatoid factors (RFs), inflammatory cytokines, and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) aiding RA. In RA T-cells that are also activated by the B-cells, further activates the macrophages and fibroblast and covert them into tissue-damaging cells. The activated macrophages aids in the inflammation in the joints by producing multiple chemokines and cytokines leading to RA pathogenesis.

What are the symptoms and effects of Rheumatoid Arthritis on the body?
Rheumatism is an old term used to describe rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease leading to joint destruction and deformity. Generally, RA is not fetal but the associated health complications like heart disease and respiratory disorders can lead to higher mortality rates. The disease appears in people age 23 to 60 years and commonly affect women 3 times more than men. There appear several RA-related complications in the patient including joint damage, tendon rupture, cervical myelopathy, and carpal tunnel syndrome. While other associated inflammatory problems include sexual dysfunction, pericarditis, vasculitis, pleuritis, and scleritis. As mentioned earlier, RA is a chronic disease so the treatment mostly involves reducing the pain, avoid or limit the damage to the joints, improve joint function to enhance the quality of life of a patient.
The sign and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include swelling in joint areas, tender, and warm joints, stiffness specially in the morning times or after physical inactivity, loss of appetite, fatigue, sweating, and fever. At an early stage, the disease mainly affects small joints of fingers and toes but as it progresses the symptoms spread to other joints including knees, hips, ankles, wrists, elbows, and shoulders. Mostly the joints of both sides of the body are affected at the same time. Besides joint RA also affect other body systems including the circulatory system, respiratory system, cardiovascular system, skin, kidneys, bone marrow, salivary glands, nerve tissues, and eyes.
Rheumatoid arthritis occurs due to an attack of the immune system on the synovium lining of the joints. The inflammation of this synovium leads to its thickening that ultimately damages the involved joint and cartilage. Also, tendons and ligaments holding the joints are weakened with time due to continuous stretch leading to loss of joint shape and alignment.
Several risk factors may increase the risk of rheumatoid arthritis including age, sex, family history, obesity, certain environmental exposures, and smoking. Rheumatoid arthritis also increases the risk of developing various health conditions including osteoporosis, rheumatoid nodules, infections, dry eyes, altered body composition, dry mouth, heart issues, lymphoma, lung disease, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
Diagnosis at an early stage is important in slowing down the rheumatoid arthritis progression and symptom relief to improve the quality of life of a patient.
What changes in diet can help improve symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Diet can not heal rheumatoid arthritis but adding the right food into your routine can surely control the inflammation and symptoms. Also maintaining a healthy weight by taking a balanced diet consisting of fresh fruits, vegetables, fatty fish, nuts, beans, olive oil, whole grains, and good fat is good for patients with RA.
Changes in lifestyle which can help Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis-related complications can be improved by making some lifestyle changes.Starting a regular exercise can improve the stiffness in the joints that can get worst with time leading to damaged muscles and tendons. Developing a habit of regular exercise and relieve pain and may also prevent or reverse the disease symptoms. On the other hand, if there is an increase in the pain or symptoms it is better to stop the exercises and give your body rest. The medication used for rheumatoid arthritis may lead to liver damage so it is advisable to discuss with your doctor the amount of alcohol, wine or beer a person consumes. Smoking is a risk factor of rheumatoid arthritis and limiting quitting tobacco use may improve symptoms.
Possible alternative remedies for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Lifestyle changes and various home remedies may also improve the onset of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Apply of heat or cold is recommended to ease pain in RA and relaxation of the muscles. Cold can reduce the swelling in the affected body part and also decrease pain sensation. Also, the RA patient should reduce the symptom-associated stress by including deep breathing to relax and improve pain. Similarly, adding yoga and meditation, and proper sleep improves mood, reduces fatigue and pain in patients. Acupuncture, massage, practicing mindfulness, joining support groups, adding probiotic supplements, fish oil supplements, applying lemongrass essential oil, and improving diet can greatly enhance the quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis patients.